The monkeypox virus appears to have mutated at an unprecedented rate, according to researchers investigating the genetic make-up of the disease.
In a new study published in the medical journal Nature Medicine, Portuguese researchers found 50 genetic mutations in the viruses they studied, when normally five to 10 would be expected.
The team collected 15 monkeypox viruses, mostly from Portugal, and reconstructed their genetic data.
On their findings, they said that this “is more than one would expect considering previous estimates”, with the figure between six and 12 times more than previous studies of other orthopoxviruses, of which monkeypox is a type.
Researchers believe their results might suggest a case of “accelerated evolution”.
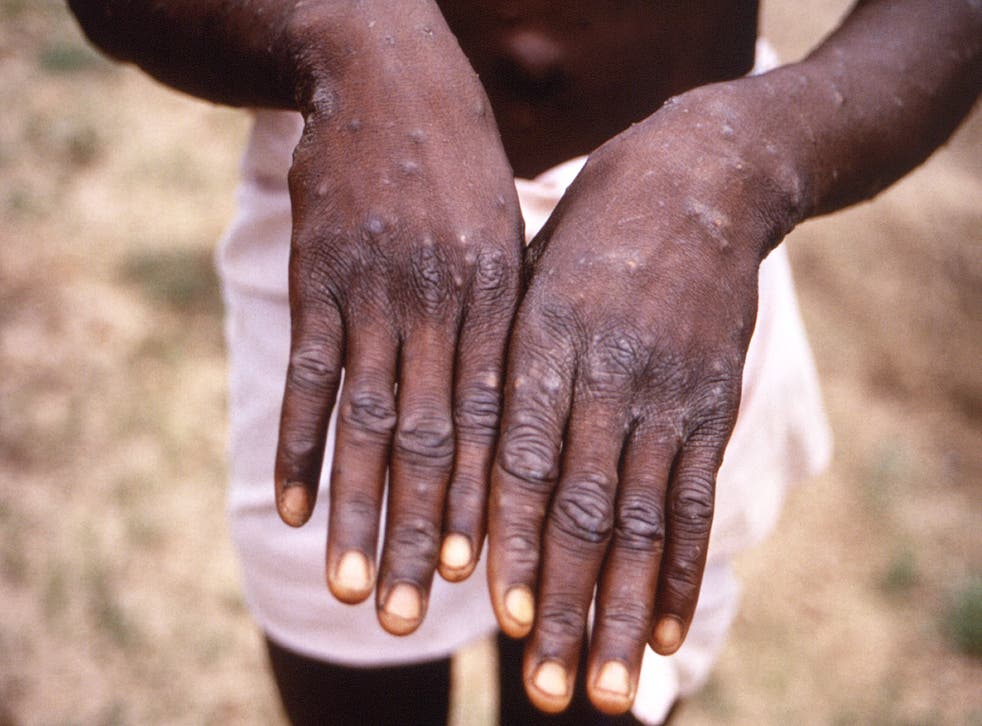
Monkeypox causes lesions on the skin
(Centres for Disease Control and Prevention)
João Paulo Gomes, head of the Genomics & Bioinformatics Unit at the National Institute of Health in Portugal, who co-authored the study, said the number of mutations was “quite unexpected”.
“Considering that this 2022 monkeypox virus is likely [to be] a descendant of the one in the 2017 Nigeria outbreak, one would expect no more than five to 10 additional mutations instead of the observed about 50 mutations,” he told Newsweek.
“We hope that specialised groups will now perform laboratory experiments in order to understand if this 2022 virus has increased its transmissibility.”
More than 3,500 cases in 44 countries had been reported as of Thursday, according to the US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The virus has been spreading in Europe
(UK Health Security Agency/AFP)
As of Monday, there were 793 confirmed cases of monkeypox in the UK, with 766 cases in England alone.
Monkeypox is a rare disease, believed to originate in animals, that causes skin lesions. It comes from the same family of viruses as smallpox and is endemic to certain parts of West and Central Africa.
However, this year has seen the first multi-country outbreak in places where the virus does not usually spread, including cases without known links to West or Central Africa.
According to the CDC, the virus can spread through direct contact with lesions, respiratory droplets, clothing, with an infected person or animal and sharing of bodily fluids.
Symptoms of the virus include fever, headache, muscle aches, swollen lymph nodes and a rash that can look like pimples or blisters.